
How to Block Applications from Accessing File Shares in ThreatLocker?
This document outlines the step-by-step process of how to block applications from accessing file shares in ThreatLocker Dashboard.
This article is a part of our ThreatLocker How-to Guides series, Chapter 06 – Network Control & Ringfencing.
Introduction
Some applications should not be allowed to access network file shares, especially those that don’t require it for normal operation. Blocking this access reduces the risk of unauthorized data exposure, ransomware propagation, and lateral movement.With ThreatLocker Application Control, you can ringfence applications and define exactly which file paths (including file shares) they are allowed or denied to access.
Implementation
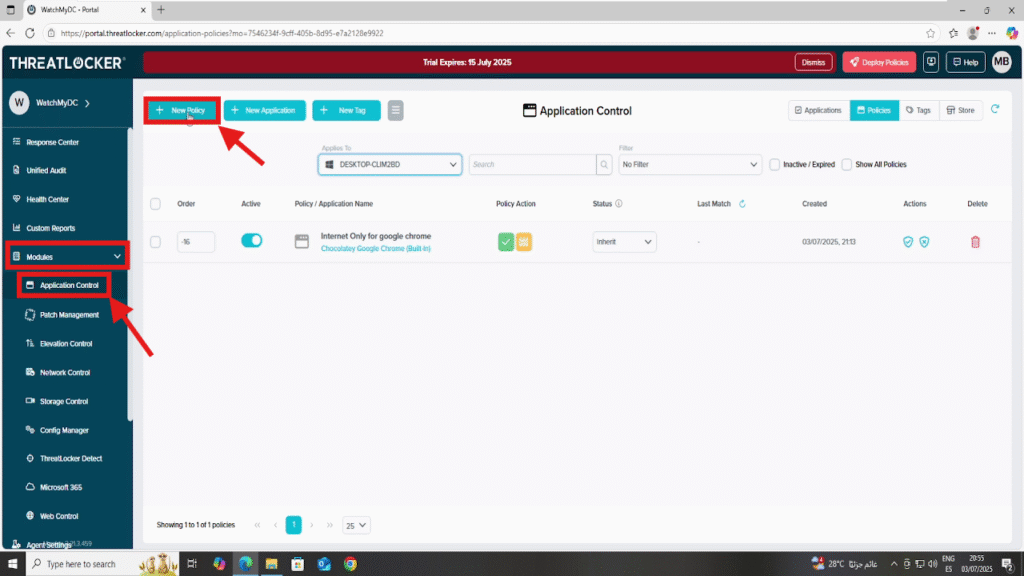
Step 1: Access the Application Control Module
- Log in to the ThreatLocker Portal.
- Navigate to Modules > Application Control
- Click Create Policy
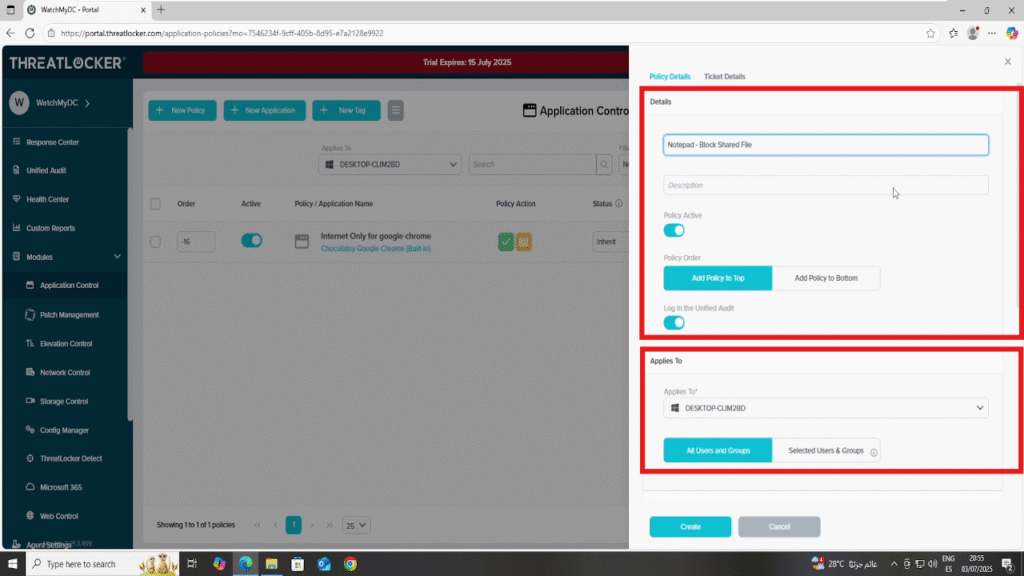
Step 2: Create the Application Control Policy
- Fill the policy form
- In the Details section
- Name: Notepad – Block File Share Access
- Description: Restrict Notepad from accessing shared network folders
- In the Applied To section
- Select the target computer or computer group where the policy should apply
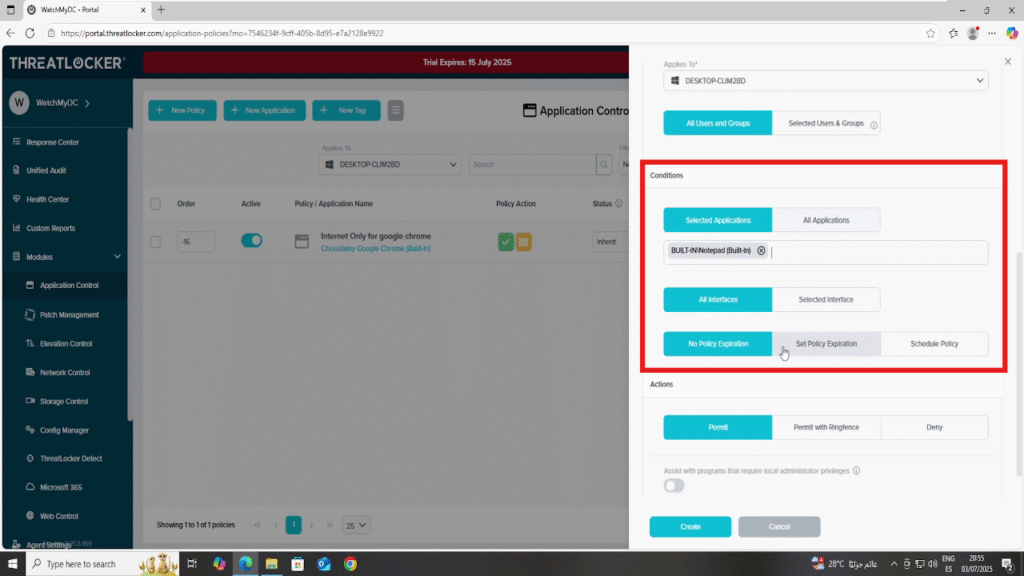
- In the Condition section
- Select the application: Notepad
- Select All Interfaces
- Select No Policy Expiration to keep the rule active indefinitely.
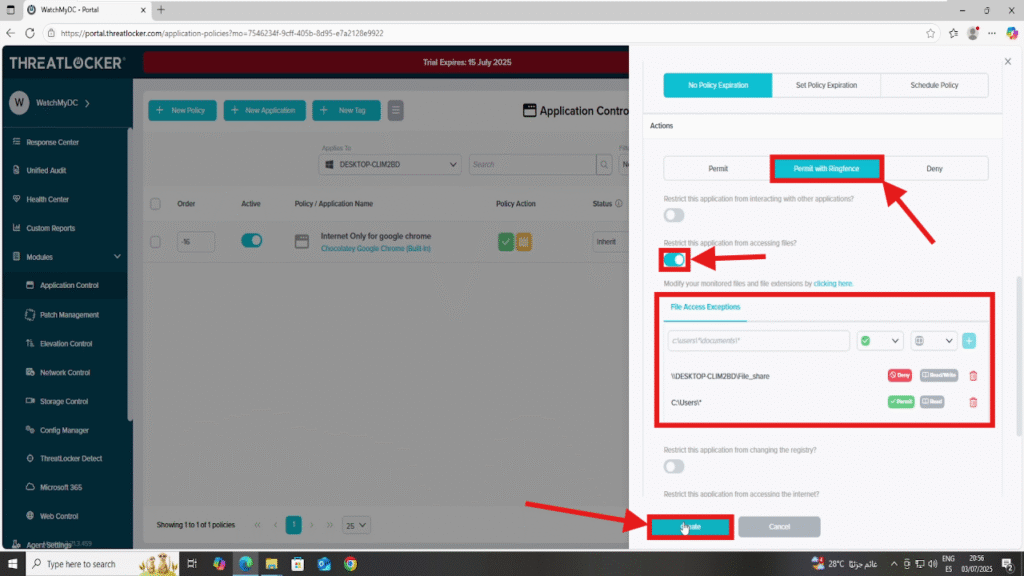
In the Action section
- Select Permit with Ringfencing
- Then activate the following setting:
- Restrict this application from accessing files
- Under the File Access Rules, configure:
- Deny access to the file share: \\DESKTOP-CLIM2BD\file_share
- Permit access to local files (This ensures the application still works properly with local documents.): C:\Users\*
2. After all fields are completed, click Create to save the policy
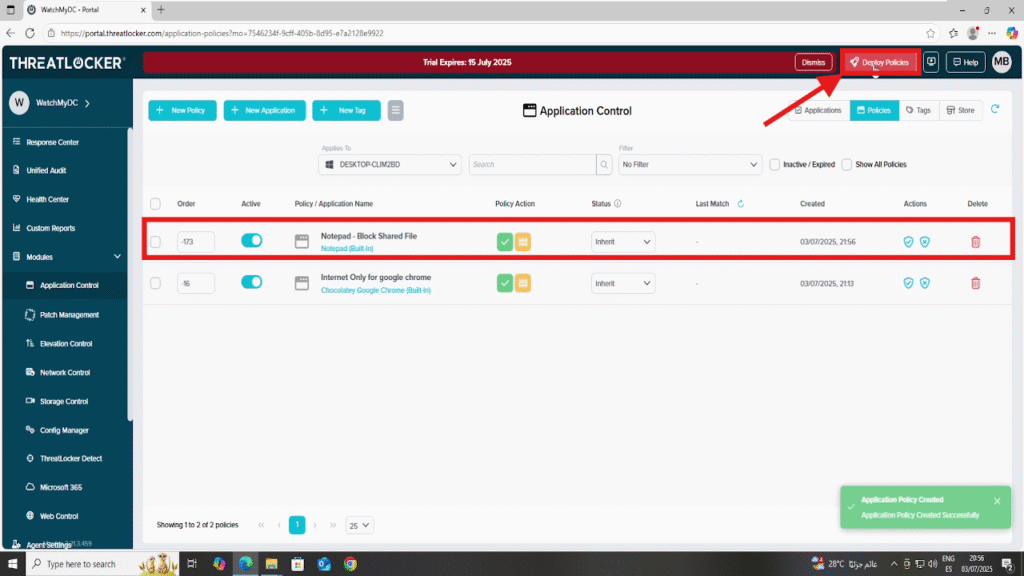
Step 3: Deploy the policy to Block Applications from Accessing File Shares
Deploy the policy to enforce it on the selected devices
Conclusion
By using ringfencing, you can prevent applications like Notepad from accessing network shares, limiting their ability to interact with sensitive or shared data.
This helps enforce Zero Trust principles, reduce risk of lateral attacks, and maintain tighter control over how applications operate across your environment.
