
How to block a specific application in ThreatLocker?
This document outlines the step-by-step process of how to block a specific application in ThreatLocker Dashboard.
This article is a part of our ThreatLocker How-to Guides series, Chapter 03 – Zero Trust Policies (Application Control).
Introduction
With ThreatLocker’s Application Control module, administrators can block specific applications on selected devices or groups.
This helps enforce a Zero Trust security model, preventing unauthorized or risky applications (e.g., PowerShell, file-sharing tools, games) from being executed on endpoints.This guide walks you through the process of blocking a specific application, such as PowerShell, using a custom deny policy.
Implementation
Step 1: Access the Application Control Module
Log in to the ThreatLocker Portal, then go to: Modules > Application Control > Applications
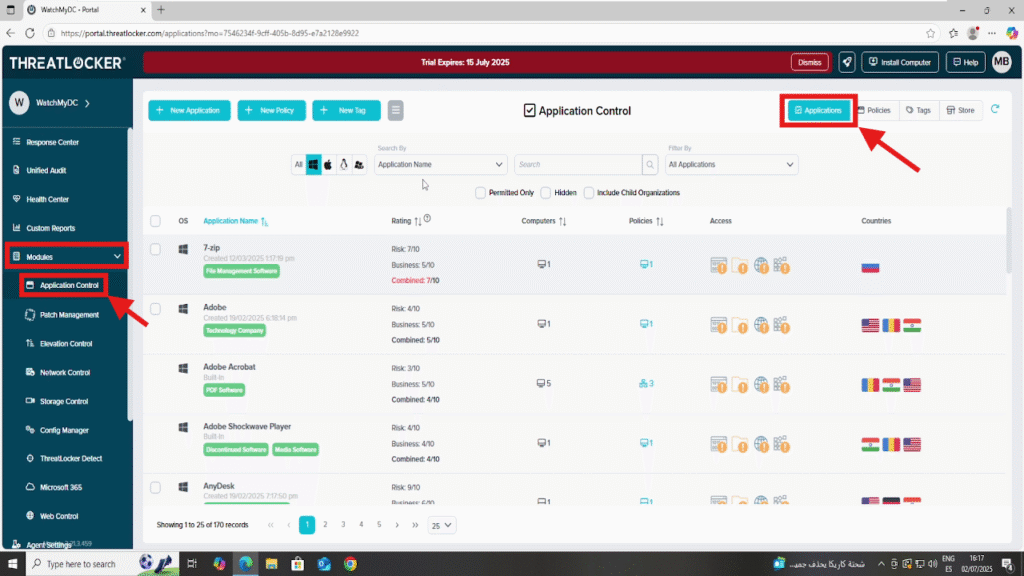
Step 2: Locate the Application to Block and Create a Policy
Use the search bar or filters (e.g., by OS: Windows, macOS, etc.) to locate the target application. In this example, we’ll block PowerShell.
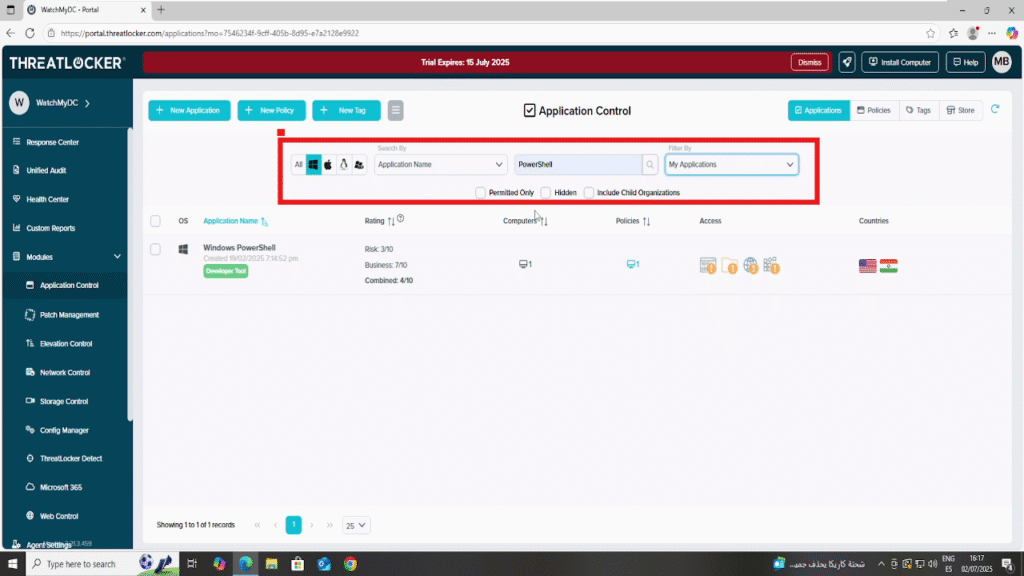
Click the application to open its details, then go to the “Existing Policies” section to view or edit current rules.
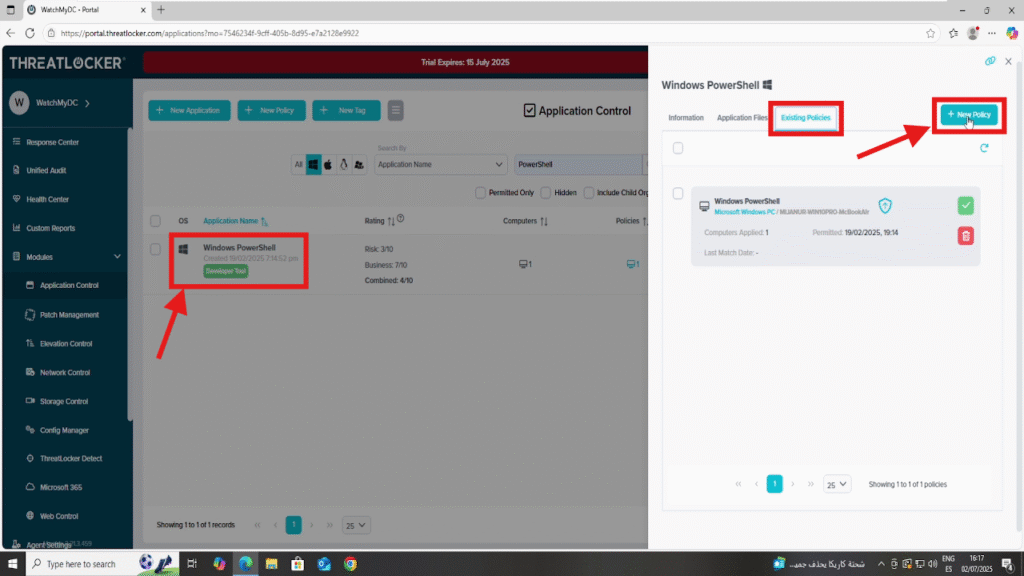
Next, select the appropriate target group or computer group where the policy should apply, and click “Continue”.
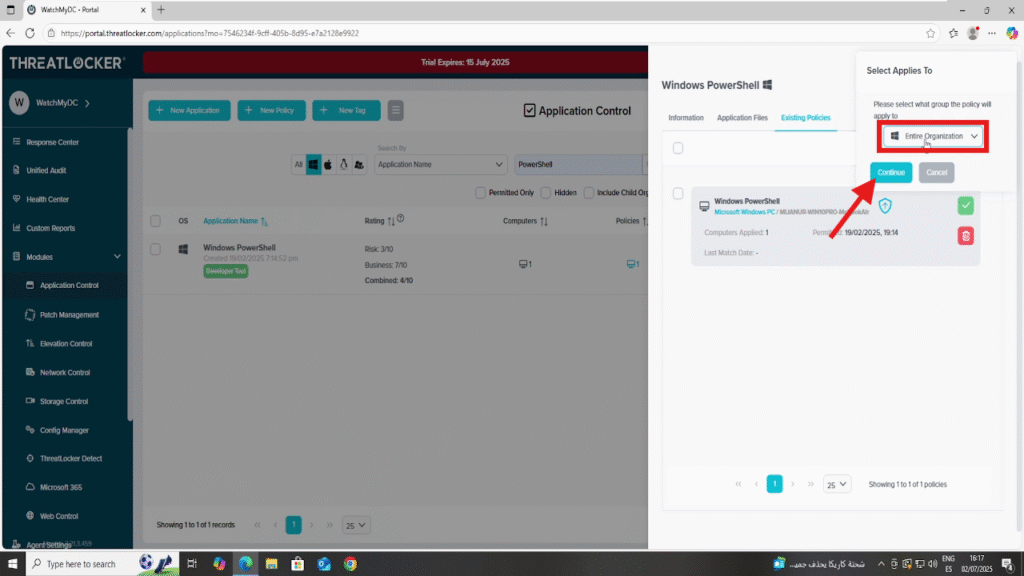
In the policy creation form, fill out all required fields, set the action to “Deny”, and choose “Show notification and allow user to request access” under User Experience.
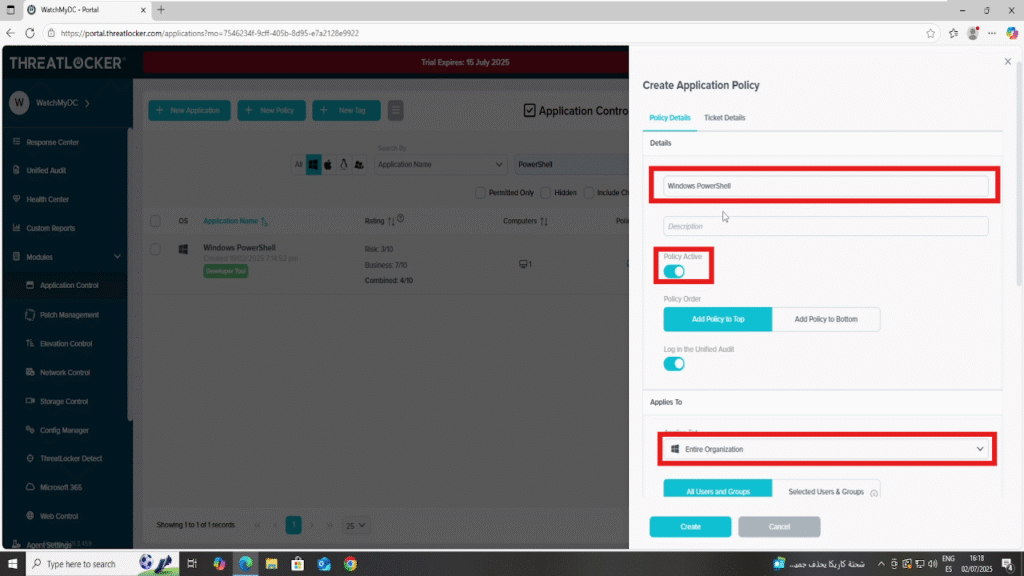
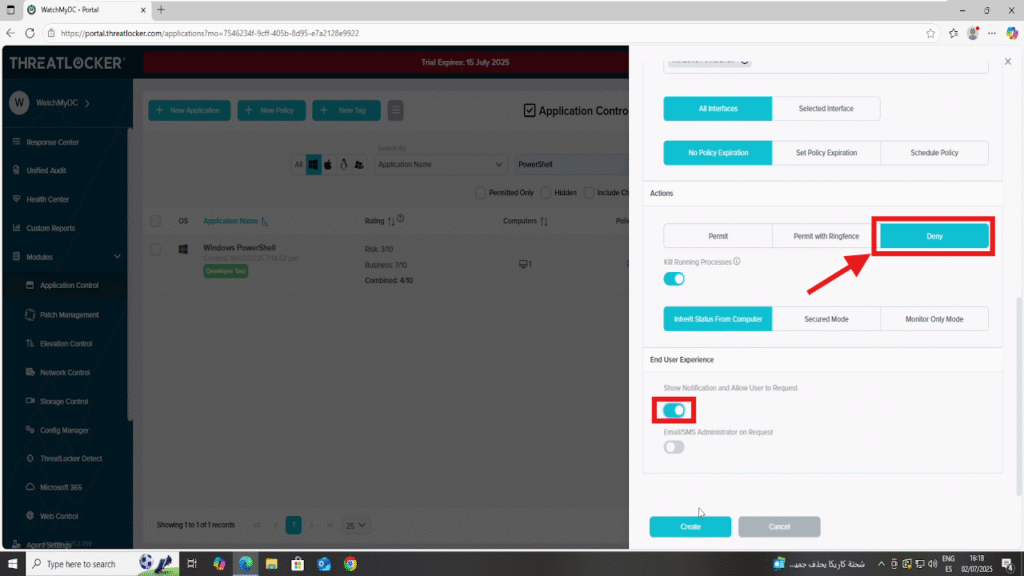
Step 3: Confirm the Policy To Block a specific application in ThreatLocker
To verify your new policy, go to Modules > Application Control > Policies. Your custom deny rule should now appear in the list, active and assigned to the target group.
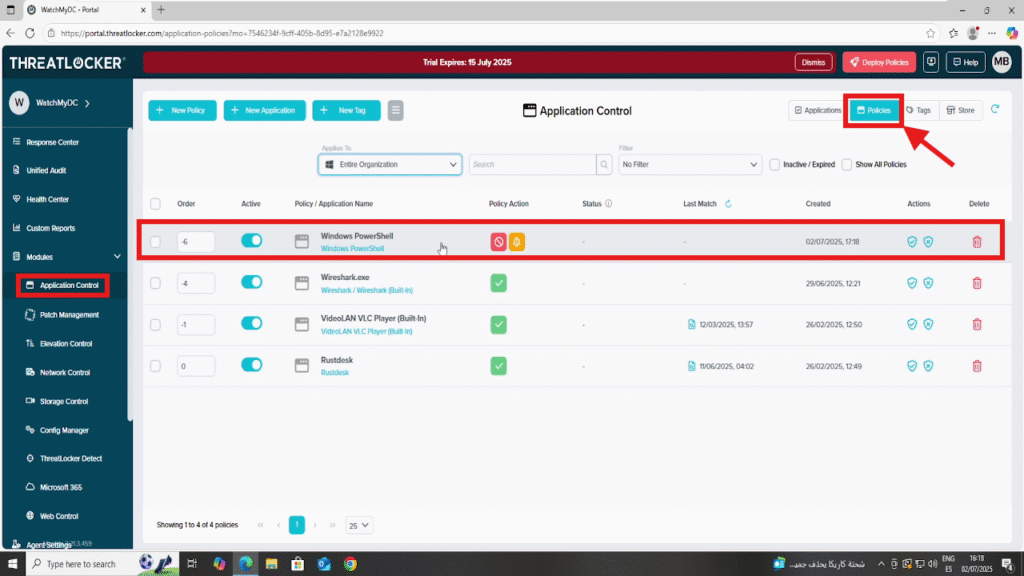
Conclusion
Blocking specific applications in ThreatLocker is essential to maintaining a Zero Trust security model.By creating a targeted deny policy, you ensure that potentially risky or unauthorized applications like PowerShell are effectively restricted across selected devices or groups.
With just a few clicks in the portal, administrators can maintain full control over the software allowed to run, while also providing a user-friendly experience through notification and access request options.
