
How to create an elevation policy?
This document outlines the step-by-step process of how to create an elevation policy in ThreatLocker Dashboard.
This article is a part of our ThreatLocker How-to Guides series, Chapter 03 – Zero Trust Policies (Application Control).
Introduction
What is an Elevation Policy?
An Elevation Policy in ThreatLocker allows users to run specific applications with administrator privileges, without giving them full local admin rights. It provides just-in-time elevation, reducing security risks while still allowing users to perform necessary tasks that require elevated access.
Objective
The objective of this guide is to show how to create an Elevation Policy in ThreatLocker.
This includes defining:
- Which users or groups can elevate,
- Which applications are allowed,
- And how to control duration, visibility, and security restrictions.
This approach helps apply Zero Trust principles while maintaining user productivity.
Implementation
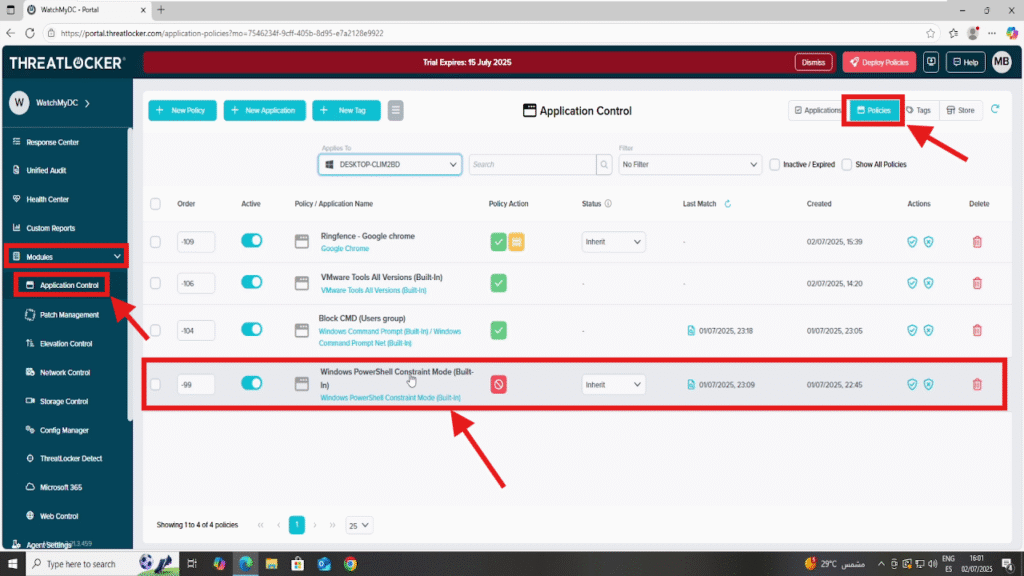
Step 1: Access the Application Control Module
- Log in to the ThreatLocker Portal.
- Navigate to Modules > Application Control > Policies.
- Locate or create the policy where you want to enable elevation. (In this example, we’ll modify the policy for PowerShell.)
- Click on the policy to open the configuration panel.
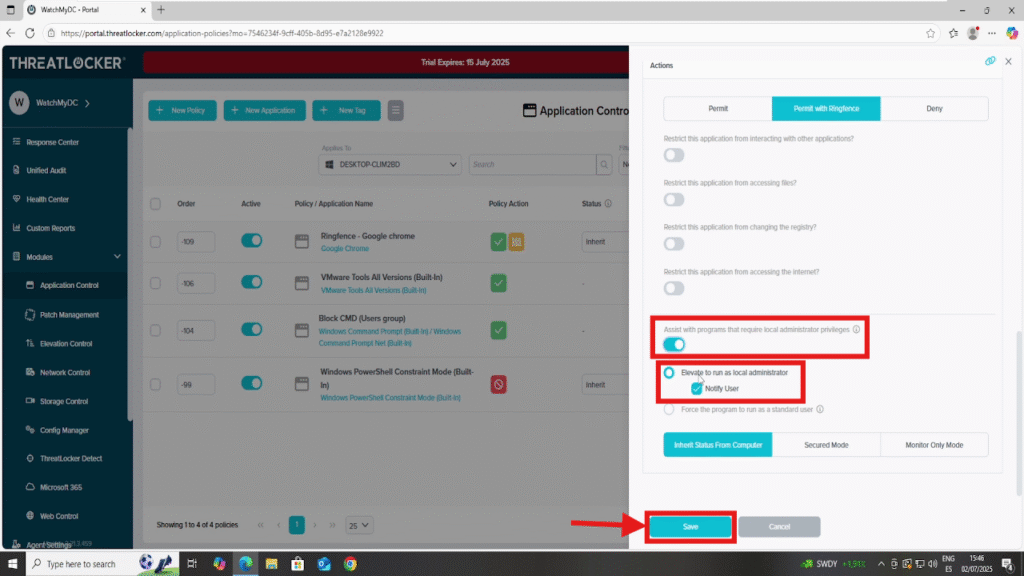
Step 2: Edit the Action Section
- 1. In the Action section of the policy:
- Select either Permit or Permit with Ringfencing, depending on your intended level of control.
- Then, enable the option: “Assist with programs that require local administrator privileges”.
- 2. Once this option is activated, choose one of the following elevation behaviors:
- Elevate to run as local administrator – Grants the necessary rights to run the application with admin privileges.
- (Optional) Enable Notify User to display a prompt indicating that elevation has occurred.
- Force the program to run as a standard user, Use this option if you want to explicitly block elevation and enforce standard privileges.
3. Once all options are configured, click Save to update the policy.
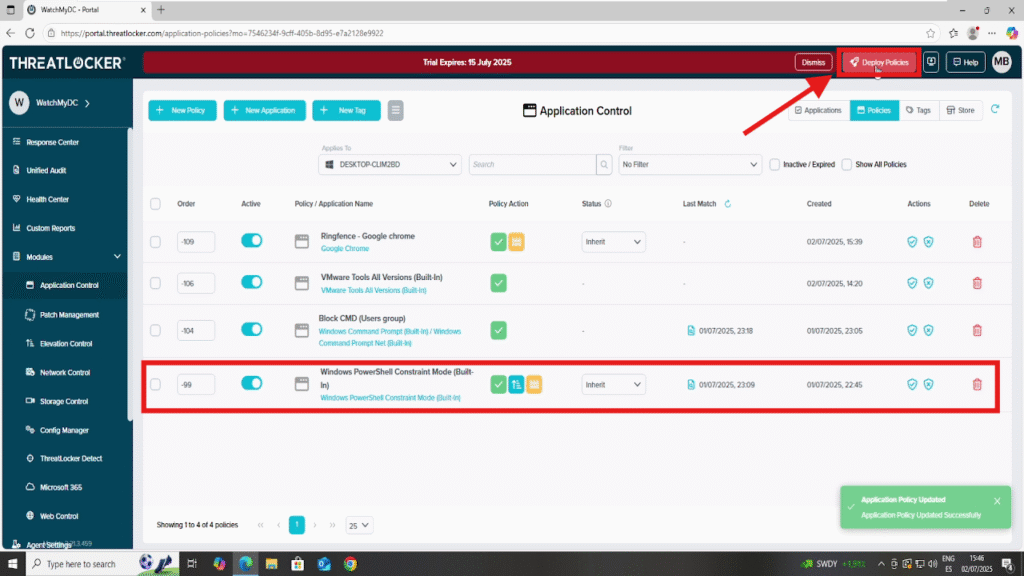
Step 3: Deploy the Policy To create an elevation policy
After making your changes, click the “Deploy” button to apply the updated policy to all relevant endpoints.
Conclusion
The use of elevation policies in ThreatLocker allows administrators to grant application specific administrator privileges without compromising overall system security.
By carefully selecting the target application, users, and elevation mode, organizations can maintain operational flexibility while enforcing strict access control. Once the updated policy is deployed, elevated access is applied securely and transparently, aligning with Zero Trust best practices.
